Privilege Escalation
Bismillah...
Privilege escalation is the act of exploiting a bug, design flaw or configuration oversight in an operating system or software application to gain elevated access to resources that are normally protected from an application or user. The result is that an application with more privileges than intended by the application developer or system administrator can perform unauthorized actions.
Most computer systems are designed for use with multiple users. Privileges mean what a user is permitted to do. Common privileges including viewing and editing files, or modifying system files.
Privilege escalation means a user receives privileges they are not entitled to. These privileges can be used to delete files, view private information, or install unwanted programs such as viruses. It usually occurs when a system has a bug that allows security to be bypassed or, alternatively, has flawed design assumptions about how it will be used. Privilege escalation occurs in two forms:
Privilege escalation is the act of exploiting a bug, design flaw or configuration oversight in an operating system or software application to gain elevated access to resources that are normally protected from an application or user. The result is that an application with more privileges than intended by the application developer or system administrator can perform unauthorized actions.
Most computer systems are designed for use with multiple users. Privileges mean what a user is permitted to do. Common privileges including viewing and editing files, or modifying system files.
Privilege escalation means a user receives privileges they are not entitled to. These privileges can be used to delete files, view private information, or install unwanted programs such as viruses. It usually occurs when a system has a bug that allows security to be bypassed or, alternatively, has flawed design assumptions about how it will be used. Privilege escalation occurs in two forms:
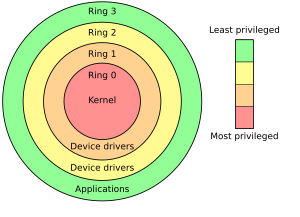
- Vertical privilege escalation, also known as privilege elevation, where a lower privilege user or application accesses functions or content reserved for higher privilege users or applications. This type of privilege escalation occurs when the user or process is able to obtain a higher level of access than an administrator or system developer intended, possibly by performing kernel-level operations. Examples:
- In certain versions of the Linux kernel it was possible to write a program that would set its current directory to /etc/cron.d, request that a core dump be performed in case it crashes and then have itself killed by another process. The core dump file would have been placed at the program's current directory, that is, /etc/cron.d, and cron would have treated it as a text file instructing it to run programs on schedule. Because the contents of the file would be under attacker’s control, the attacker would be able to execute any program with root privileges.
- Cross Zone Scripting is a type of privilege escalation attack in which a website subverts the security model of web browsers so that it can run malicious code on client computers.
- Some versions of the iPhone allow an unauthorised user to access the phone while it is locked.
- Internet Banking users can access site administrative functions or the password for a smartphone can be bypassed.
- Horizontal privilege escalation, where a normal user accesses functions or content reserved for other normal users. Horizontal privilege escalation occurs when an application allows the attacker to gain access to resources which normally would have been protected from an application or user. The result is that the application performs actions with the same but different security context than intended by the application developer or system administrator; this is effectively a limited form of privilege escalation (specifically, the unauthorized assumption of the capability of impersonating other users). Examples:
- User A has access to his/her bank account in an Internet Banking application.
- User B has access to his/her bank account in the same Internet Banking application.
- The vulnerability occurs when User A is able to access User B's bank account by performing some sort of malicious activity.
- This malicious activity may be possible due to common web application weaknesses or vulnerabilities.
Comments
Post a Comment